

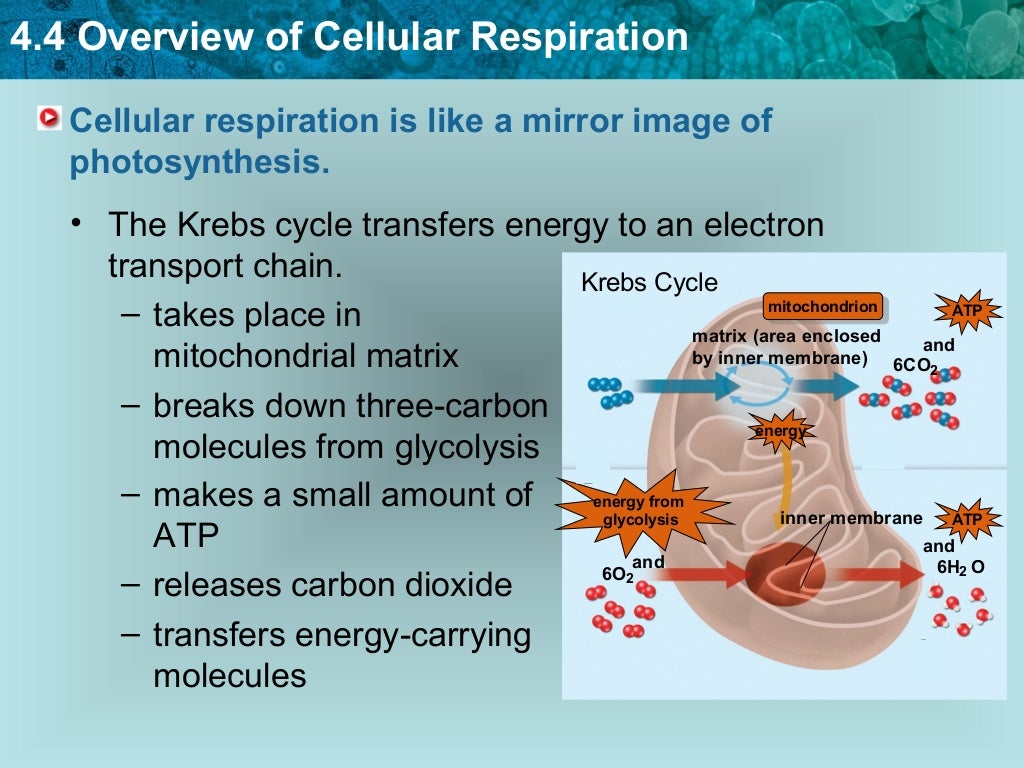
The conversion of fatty acids (from lipids) or amino acids (from proteins) into glucose or intermediate products is called gluconeogenesis (p. If all glycogen supplies are depleted, then other substances in the body are converted into glucose or intermediate products that can enter the above-outlined cellular respiration pathway. When glucose levels drop between meals, the hormone glucagon is released from the pancreas and stimulates the conversion of glycogen into glucose (by the process of glycogenolysis). When glucose is in adequate supply, such as shortly after consumption of a meal, the hormone insulin from the pancreas increases glycogen formation ( glycogenesis) in the liver. The above notes describe the process of carbohydrate (glucose) catabolism for the production of ATP. 6 H 2O are formed when the electrons unite with O 2 * at the end of electron transport chain.net yield of 34 ATP per glucose molecule.The H + ions then flow back through special pores in the membrane, a process that is thought to drive the process of ATP synthesis.
#CELLULAR RESPIRATION OVERVIEW SERIES#
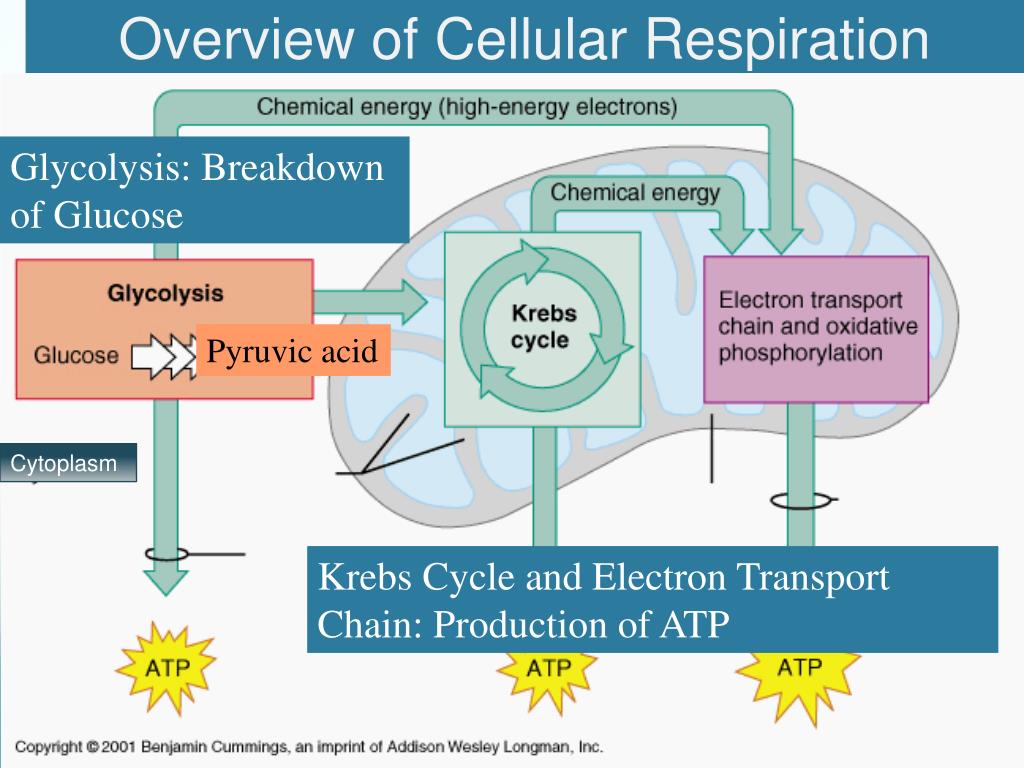
net yield of 2 ATP per glucose molecule.an anaerobic process - proceeds whether or not O 2 is present O 2 is not required.converts each molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvic acid (a 3-carbon molecule).a ten-step process that occurs in the cytoplasm.Pay special attention to bold and underlined terms.Ĭellular respiration is the enzymatic breakdown of glucose (C 6H 12O 6) in the presence of oxygen (O 2) to produce cellular energy (ATP): Please be familiar with this material before we reach those topics in lecture. This subject may not be covered in the lectures, but you are responsible for all of the information in these notes because it is important background for topics in this course, suchas muscle cell physiology (Chapter 7). NOTE: It is expected that you have studied this topic in High School Biology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
